1 Introduction
Since Dr. Holonyak of General Electric Company of the United States invented the world's first light-emitting diode (LED) in 1962, the effort to make the LED emit all-color visible light has not stopped. LEDs made of AlGaInP materials can cover a range from red light (650 nm) to yellow light (580 nm). In 1993, Nakamura of Japan solved the doping problem of p-type GaN and successfully developed a GaN-based blue LED. Based on this, the LED spectrum made by AlGaInN covers the range from near ultraviolet (380 nm) to green (530 nm). Range [2]. Now, LEDs cover almost all areas of visible light. LEDs are widely used.
1.1 Development and main applications of GaN-based LED devices
In 1993, Nichia developed the first high-intensity GaInN/AlGaN heterojunction blue LED with a luminance of more than 1 cd [3]. With the improvement of metal organic vapor deposition epitaxy (MOCVD), high-brightness and high-power LEDs Products have been developed. There are two kinds of LED products, as shown in Figure 1 (a), (b), one is a small-die LED, the die power is about 0.06W, the chip size is 350μm × 350μm, and the other is a large-die LED. The die power is 1-3W, and the chip size is 1mm×1mm. In recent years, the luminous efficacy of LEDs has increased from 50 to 60 lm/W, and last year's low-power LEDs have exceeded 170 lm/W, which is more than the efficacy of all existing lighting products. As a light source, LED has obvious advantages compared with other illuminating light sources, such as energy saving, environmental protection, green health, and long life. With the development of high-power, high-brightness LEDs, their use has become closer to our lives. The main uses of LEDs are in six categories:
(1) Display: It is mainly LED display, etc.;
(2) Backlight: LCD backlight, LED energy saving, environmental protection, longevity, low voltage and other characteristics are very suitable for LCD backlights;
(3) Special lighting: including flashlights, miner lights, spotlights, Christmas lights, etc.;
(4) Urban lighting; landscape lighting: street lights, landscape lights, etc.;
(5) Automotive lighting: At present, the third lighting, interior lighting, instrument panel lights, etc., but with the improvement of brightness, light efficiency, etc., including rear lights, license plate lights, rear view mirrors, etc. Even the headlights, etc. have begun to adopt LEDs;
(6) General lighting: The general lighting market includes all kinds of general lighting fixtures, lighting sources, etc. It is the ultimate target market for high-power white LEDs and the largest market.
The Chinese lighting industry has experienced rapid development in recent years. According to authoritative statistics, the total sales of the domestic lighting industry in 2000 was 55 billion yuan. In 2001, it exceeded 68 billion yuan. In 2002, it reached 80 billion yuan. In 2003, it reached 95 billion yuan. In 2004, it exceeded 110 billion yuan. In 2005, it reached 110 billion yuan. 140 billion yuan, a rapid increase of nearly 20% for five consecutive years. In addition, the export of China's lighting electrical products has continued to grow in recent years, with an average annual growth rate of more than 20%. In 2004, the export volume of the whole industry reached 6.65 billion US dollars, which is exported to more than 150 countries and regions in the world.
According to conservative estimates, the size of China's lighting market will exceed 220 billion yuan in 2010. If LEDs account for 10% of the market, it will be a market size of 22 billion yuan, and the demand for high-power LEDs will reach 1.5-200 million.
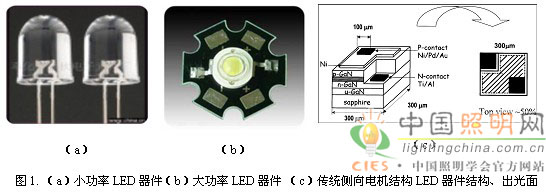
1.2 Research Status of GaN-Based LED Devices <br> Today's LED devices are mainly grown on sapphire substrates. With the maturity of MOCVD technology and the stability of LED device fabrication processes, LED devices for sapphire substrates The light effect is also gradually improving. For the traditional structure of LED devices, the current domestic mainstream LED products have generally achieved a luminous efficiency of 50-70 lm/W, even under the existing relatively perfect growth level, it is difficult to have The increase is greater, mainly due to the limitations of the traditional LED device itself.
(1) Structural limitations of sapphire substrates:
We all know today GaN-based material is grown on a sapphire substrate, however, the difference between the sapphire substrate and the conductive lattice mismatch with GaN material problems brought today's popular LED device is not more Avoiding defects.