The Polar code was adopted as the control channel code of the 5G eMBB scene. The two days were continuously screened by this message, and even the people who eat melons are very good.
However, as the media reports continue to ferment, the truth has changed in word of mouth, and there is no lack of exaggeration and suspicion. Xiao Bian finally can't sit still, and wants to confide in the snacks, hoping to stand as objectively as possible. In this impetuous world, a little insignificant sound, the voice of a communications engineer.
The event goes back through us...
From November 14 to 18, 2016, the 3GPP RAN1 #87 conference was held in Reno, USA. One of the contents of this conference was to determine the channel coding scheme for 5G short code blocks. Among them, three short code coding schemes were proposed: Turbo code, LDPC code and Polar code.
Regarding the battle for these three coding schemes, this is already the second contest of the 5G standard. At the meeting held in Lisbon, Portugal, on October 14, 2016, the LDPC code defeated the Turbo code and the Polar code and was adopted as the long code block coding scheme for the data channel of the 5G eMBB scene.
In this context, this debate on the short code block coding scheme is more intense. Because the LDPC code has taken the next round, for the implementation complexity, the entire mobile communication system adopts a single coding scheme to facilitate 5G deployment. For example, 3G and 4G use Turbo codes, and it is estimated that more people will support LDPC codes. .
In this way, the LDPC code mainly led by American companies may be unified in 5G world, and the Polar code led by Chinese companies such as Huawei will be abandoned.
Since the call for abandoning the Turbo code is louder, after the last meeting lost, it can be said that the basic trend of the Turbo code has gone. This 5G coding battle eventually evolved into a boxing match between the Polar code and the LDPC code, a Sino-US boxing hegemony. Race.

In the end, after a continuous day and night battle, the Polar code finally regained a game on the 5G core standard and became the control channel coding scheme for the 5G eMBB scene.

Since then, after two fierce battles, in the 5G eMBB scenario, the Polar code and the LDPC code are divided into two parts. The former is the signaling channel coding scheme and the latter is the data channel coding scheme. The Polar code and the LDPC code go into the cellular mobile communication system historically together, and in the 3G and 4G eras, we have lost a lot of Turbo codes for many years, leaving behind a lonely and lonely back.
This is indeed an exciting news. If I say it is to turn it around, I don’t think it is too much.
This is absolutely good for Huawei and Chinese companies that dominate the Polar code. After all, the R&D investment in Polar code has finally come to the fore.
However, we have seen reports from some media, IMHO, too exaggerated.
1, not "take the 5G era"
In the 5G eMBB scenario, Polar is the signaling channel coding scheme, and the LDPC code is the data channel coding scheme, which is called the equalization. At the same time, there is still a lot to go.
The eMBB scenario we mentioned in the previous article is just one of the scenarios for 5G applications. 3GPP defines three major scenarios of 5G: eMBB, mMTC, and URLLC. eMBB corresponds to large-capacity mobile broadband services such as 3D/Ultra HD video. mMTC corresponds to large-scale Internet of Things services, while URLLC corresponds to services such as driverless, industrial automation, etc. that require low latency and high reliability.
The coding scheme adopted this time is for the eMBB scenario, and the channel coding scheme under the URLLC scenario will be determined later, and finally the mMTC scenario (estimated in the first quarter of 2017).
Although the adoption of Polar code has laid a solid foundation for the subsequent standard discourse power, the revolution has not been successful, and comrades still need to work hard.
2. The Polar code is not Huawei, and LDPC is not Qualcomm.
This starts with the history of channel coding.
The Turbo code was invented by French scientists C. Berrou and A. Glavieux. Since 1993, the field of communications has begun to study it. Subsequently, the Turbo code was adopted by the 3G and 4G standards.
The LDPC code was proposed by MIT professor Robert Gallager in 1962. This was the earliest proposed channel coding to approximate the Shannon limit. However, it was difficult to overcome the computational complexity due to the current environment and was subsequently forgotten. It was not until 1996 that it caught the attention of the communications field. Later, the LDPC code was adopted by the WiFi standard.
The Polar code was proposed by E. Arikan, a professor at the University of Birken in Turkey in 2007, and began to attract attention in the field of communications in 2009.
In short, channel coding is the original theory of mathematicians. Communication is followed by mathematicians. On the basis of their theory, they continue to study and experiment, and make it fall into practical use.
Why do some companies support Polar codes, and some companies support LDPC codes? It's like betting. If you look at some kind of coding technology, you start to study it. Once the gambling wins, then my research results can be applied quickly. Once I lose, I can only start from scratch.
For example, Huawei chose the Polar code, and 5G also chose the Polar code, which means that Huawei is more influential in the 5G field. Of course, in the research, we must have accumulated a lot of patents.
Therefore, although the Polar code won this time, the individual thought that the media should not neglect the contributions of mathematicians because they were too excited, and they could not even wear Li Dai. Some things have no national boundaries.
3. Why does 5G adopt the Polar code?
This subtitle should be called: Why does 5G adopt Polar code and LDPC code? Why did you give up the Trubo code?
Start with what is called channel coding.
When we pick up the phone and brush the circle of friends, the data is transmitted between the phone and the base station via wireless signals. Due to the influence of wireless interference, weak coverage, etc., the data sent by our mobile phone and the data received by the base station sometimes are inconsistent. For example, the mobile phone sends 1 0 0 1 0, and the base station receives 1 1 0 1 0, For error correction, mobile communication systems have introduced channel coding techniques.
Channel coding, in simple terms, is that we insert redundant bits into a K-bit data block to form a longer code block. The length of this code block is N bits, N"K, NK is used for detection and The error-corrected redundant bits, the coding rate R is K/N. A good channel coding is the theoretical limit of unlimited access to channel capacity at a certain coding rate.
In the past few decades, two channel coding techniques close to the capacity limit have emerged: LDPC and Turbo codes, which were adopted by the 3G and 4G communication standards and the WiFi standard, respectively. In 2007, Turkish professor E. Arikan proposed the Polar code, which is known as the only coding method that has been found so far to reach the Shannon limit.
Therefore, these three excellent coding technologies have entered the eyes of the 5G coding standard and triggered a competition.
Why is this competition so intense? It is a disaster caused by KPIs.
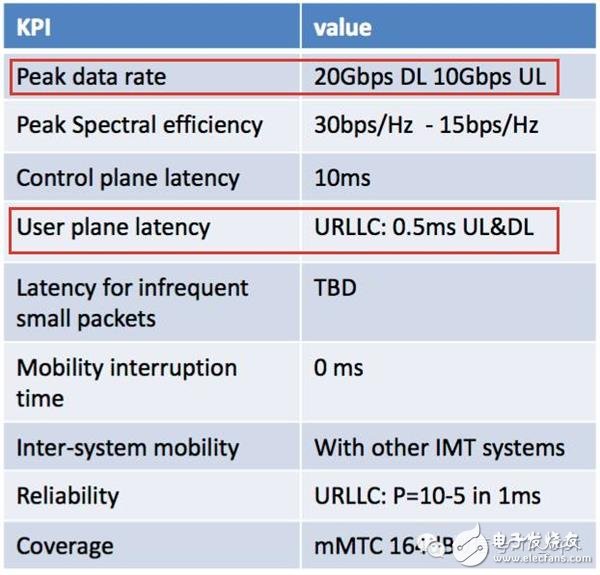
In the KPI of 5G NR (New Radio), it is clearly stated that the peak rate is 20 Gbps and the user plane delay is 0.5 ms (URLLC).
This KPI is set too high, which is 20 times higher on the basis of 4G. Report leadership, not good enough.
How hard is it? The downlink peak rate requirement of 5G NR is 20Gbps. Since each bit received by the mobile phone (or base station) passes through the channel decoder, 20Gbps is equivalent to the decoder processing billions of bits of data per second.
For example, 20 Gbps means that the decoding throughput T is 20 Gbps. Assuming that the decoding iteration number I is 10 and the processor clock frequency F is 500 MHz, then I *T /F = 10*20G/ 500M=400, which means that 400 processors need to work in parallel.
(Note: The decoder is the most difficult part of channel coding)
This is one of the reasons why many people choose to abandon the Turbo code used in the 3G and 4G eras, because the maximum rate of 4G is only 1 Gbps. The traditional Turbo code is iteratively decoded, which is essentially derived from the internal structure of the serial. Therefore, some people think that Turbo encountered a bottleneck when it encountered a higher rate of 5G.
For example, the LDPC decoder is based on the parallel internal structure, which means that the decoding can be processed in parallel at the same time, which can not only handle a large amount of data, but also reduce the processing delay. Although external parallelism can be used, it introduces latency issues.
For the delay, for the instinct of the technical house, please allow me to take another look.
The URLLC application scenario of 5G NR requires a user plane delay of 0.5ms, which is one-twentieth of 4G 10ms. The reason why such a high delay is required is that when we experience services such as augmented reality, remote control, and games, we need to transmit them to the cloud for processing and return them in real time. This round-trip process delay must be low enough to be low enough. The user is not aware of it. In addition, the machine is more sensitive to time delay than humans, and has higher requirements for delays, especially for 5G car networking, automatic factories and remote robots.
The 0.5ms delay of the air interface means that the delay of the physical layer cannot exceed 50μs, and the physical layer delay is affected by other factors (such as synchronization) except for the decoding, so the processing delay required for decoding must be lower than 50μs, the lower the better.
In general, this is like a flight during the Spring Festival. There are too many people. It is necessary to transfer hundreds of millions of Chinese people from south to north and from east to west. The amount of data is too large, which requires more flights and faster navigation. speed.
The “flight company†5G NR indicates that Yalishan is large, and the channel coding indicates that the pressure is greater and the layers are transmitted.
However, this pressure is not enough, 5G said it can resist.
Just now we talked about 3GPP defined 5G three scenarios: eMBB, mMTC and URLLC. These scenarios correspond to 5G AR, VR, car networking, large-scale Internet of Things, high-definition video and other applications, compared to 3/4G. For voice and data services, 5G can be much more busy.
This puts higher requirements on 5G channel coding, and needs to support a wider code block length and more coding rates. For example, short code blocks are used in the Internet of Things, long code blocks are used in high-definition video, low coding rates are used in rural stations where the base station is sparsely distributed, and high coding rates are applied to dense urban areas. If everyone uses the same coding rate, this will result in wasted data bits and waste spectrum resources. This is called coding flexibility.
In addition, 5G has to guarantee higher reliability communication. The air interface error rate of LTE for general data requires an initial transmission of 10%. After several retransmissions, the error block rate is less than 1%. However, 5G requires the block rate to drop to one in 100,000. This means that in the 100,000 code blocks, only the channel decoder is allowed to make one mistake, and at most one code block can not be corrected.
In summary, the factors that determine which encoding method 5G uses are: decoding throughput, delay, error correction capability, flexibility, and implementation complexity, maturity, and backward compatibility.
Comparing the decoding throughput, delay, error correction capability, flexibility and implementation complexity of the three codes, who is stronger?
Xiao Bian consulted the latest large amount of literature, and the result was: it was confused and turned into a face. This problem is too complicated, and it is said that the public priest is reasonable.
For example, some people think that the Turbo code has reached the bottleneck and cannot handle the 20Gbps high rate. However, some manufacturers have proved that the Turbo decoder based on the full parallel design can achieve a decoding throughput of 21.9 Gbps and a processing delay of 0.24 μs. This also meets the 20Gbps rate requirement of 5G NR.
For example, if the computational complexity is measured by the total number of Max, Min, and Add operations performed by the decoder in decoding each bit, it is considered that the Polar code and the LDPC code are superior to the Turbo code in computational complexity.
For example, some people say that Turbo is not flexible enough. However, it has been pointed out that LTE Turbo codes have a code block length of 40 to 6144, a total of 188 types, which can support different services, and multiple parallel processors to complete code block decoding at the same time. Turbo code, more flexible to support different block lengths.
...
Xiao Bian tried to find the reason for 5G to choose Polar code or LDPC code from the technical point of view. However, the ability is limited, and he has made himself sloppy.
So, let's look at maturity and backward compatibility.
The Turbo code is adopted by the 3/4G standard, the LDPC is adopted by the Wi-Fi standard, and the Polar code appears later, and there is no standard before the 5G. In this respect, the maturity of the Polar code is low.
However, Huawei expressed dissatisfaction. Before the dispute over the 5G coding standard, there was an article in the overseas communication circle. Huawei said that the 5G rate reached 27Gbps with the Polar code, indicating that it is no problem to meet the 5G demand.
As for backward compatibility, 5G NR is a brand-new wireless technology, which is a new generation. It is not like 2G-"2.5G or 4G-"4.5G, the current network can be upgraded. This is for operators to buy new base station equipment. So, in fact, do not have to consider backward compatibility.
However, for the terminal is another matter. Today's 4G phones support 2G and 3G. Similarly, 5G phones will support 3G and 4G in the future. 3G and 4G use Turbo code. If 5G also uses LDPC or Polar code, this means that the mobile phone needs to adopt two sets of hardware design, and the decoder is an important part of the whole baseband processor, accounting for nearly 72% of baseband processing. Hardware resources and power consumption, which may cause the cost of 5G terminals to be slightly higher, or it may slightly lengthen the commercialization time of 5G.
However, there is an old saying that sharpening the knife does not mistake the woodworker. If this coding scheme is good enough and has great potential, then what is the relationship between 5G and night is nothing more than spending a little more time for a better experience.
So, regarding why 5G adopts Polar code, our conclusion is:
Technical analysis is not useful.
Because, this standard dispute, in our view, has already surpassed the boundaries of technology, but the contest between comprehensive strength and discourse power.
The Polar code will eventually win, only to illustrate the rise of China's communications, and its international status has improved significantly.
Parallel Actuator,Mini Electric Actuator,Linear Drive Actuator,Electric Actuator Controller
Kunshan Zeitech Mechanical & Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.zheteswitches.com