On the CAN-bus network, CAN messages are sent in broadcast form. CAN messages do not contain address information. Whether or not to process received CAN messages is determined by the software at the receiving point. CAN-bus only provides reliable message transmission services. The use of CAN messages is defined by the user. Therefore, nodes in the CAN network must establish a unified rule to communicate with each other. The CAN application layer protocol is such a rule.
This rule defines the use of frame IDs and frame data in CAN messages. For example, the frame ID is defined as the address of the CAN node that needs to process the frame data. According to different applications, there are many kinds of CAN application layer protocols in the world. Common CAN-bus application layer protocols are as follows:
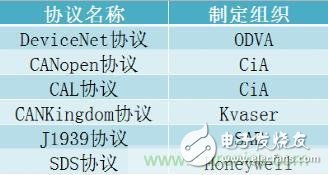
figure 1
Next, we look at how to build a CAN-bus application layer protocol
l To build a fieldbus network, the key technical problems to be solved are:
l The speed, capacity, priority level, node capacity, etc. of the information transmitted by the bus;
l reliable data transmission under high electromagnetic interference environment;
l Determination of the delay size at the maximum transmission distance;
l network fault tolerance technology;
l Network monitoring and fault diagnosis.
To solve the above problems, we must fully consider the type of bus used by the fieldbus network, because the above issues and the performance characteristics of the bus are closely related, then we look at the above characteristics of the CAN-bus bus:
l CAN-bus network transmission speeds up to 1Mbps, and the use of non-destructive arbitration, through the message identifier to indicate the message priority;
lCAN-bus adopts differential signal transmission and adopts reliable data check and error detection mechanism;
lCAN-bus adopts frame transmission, each message is allowed to transmit up to 8 bytes, and the frame structure has strict rules, which can determine the maximum transmission delay;
lCAN-bus has a reliable error mechanism and detection mechanism. The transmitted information can be retransmitted after being destroyed. The node has the function of automatically exiting the bus when the error is serious.
l The network monitoring and diagnosis can be solved through the establishment of a forbidden CAN-bus application layer protocol.
Distribution of CAN messages
Including the assignment of message identifiers and the distribution of message data, the definition of the message format is essentially a detailed description of the CAN message distribution rules.
Definition of message ID:
CAN2.0A frame: 11-bit ID
CAN2.0B frame, 29-bit ID
Definition of message data: Each frame of message contains up to 8 bytes of data
Implementation of CAN Network Data Communication
In the CAN network, the information is distinguished by the identifier of the message, so the purpose of establishing the information link is achieved by allocating various identifiers of the message.
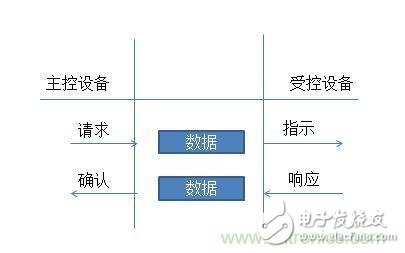
Figure 2. Command/response mode communication
CAN application layer protocol: node-oriented and message-oriented protocols
Data communication protocols can basically be divided into two types: "node-oriented protocols" and "message-oriented protocols", as shown below:
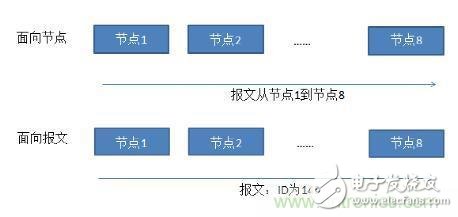
Figure 3. Node-oriented and message-oriented data communications
Develop a CAN Application Layer Protocol
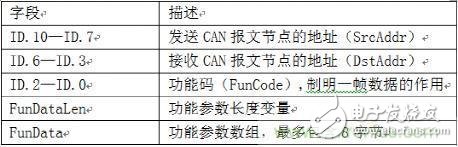
Figure 4
In order to demonstrate to the reader the development and use of the CAN application layer protocol, the following defines a simple CAN application protocol stack in which only the data frames in the CAN standard frame are used and the 11 bits in the frame ID are allocated and used. The methods are listed in the following table. The function parameter array FunData of the function parameter length variable FunDataLen is also defined in the protocol. The array can provide enough control parameters for certain specific function functions when needed.
3V Lithium Fluorocarbon Button Batteries
DADNCELL 3V Lithium Fluorocarbon Button Batteries use fluorocarbon material as the battery positive electrode. The fluorocarbon material has high thermal and chemical stability. It does not decompose at high temperature ≤600℃, and does not crystallize at low temperature. The battery operating temperature range can reach -40~125℃ ; Its chemical stability ensures the safety of the battery, so that the battery has a higher safety performance when short-circuit, collision, and extrusion, and has the characteristics of explosion-proof and spontaneous combustion. Our company uses self-developed electrolyte to make the battery life more than 10 years.
Our BR series button batteries are conventional high and low temperature resistant button batteries, and the working temperature is -40℃~+85℃
Accepts customized upgraded version of high and low temperature resistant button battery, working temperature is -40℃~ +125℃
Battery application range: It can be used in fields that have strict requirements for high and low temperatures and high energy density. For example, automobile tire pressure gauge (TPMS) battery, industrial control motherboard battery, computer motherboard battery, smart instrument battery, oil field drilling platform emergency equipment power supply, marine life-saving flasher, implantable medical battery, etc.
3V Lithium Fluorocarbon Button Batteries,Wide Working Temperature Rang Cells,3V Coin Cells For Computer Motherboard,3V Li-(Cfx)N Tpms Button Batteriey
Shandong Huachuang Times Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dadncell.com