Before introducing the transaction layer, first briefly understand the communication mechanism of the PCIe bus. Suppose a device wants to read data from another device. First, this device (called a Requester) needs to send a Request to another device, and another device (called a Completer) returns data through the Completion Packet or Error message. In the PCIe Spec, there are four types of requests: Memory, IO, Configuration, and Messages. Among them, the first three are inherited from the PCI/PCI-X bus, and the fourth is the newly added type of PCIe.
Detailed information is shown in the following table:
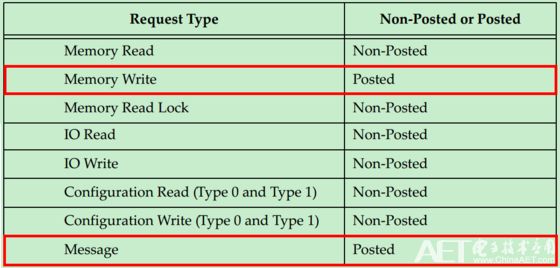
From the table we can see that only Memory Write and Message are of type Posted, others are of type Non-Posted. The so-called Non-posted, that is, after the Requester sends a packet containing a Request, it must obtain a reply to the packet containing the Completion. This transmission is considered to be over, otherwise the wait will be performed. The so-called Posted, Requester's request does not require Completer by sending a packet containing Completion to answer, of course, it does not need to wait. Obviously, Posted type operation has much higher bus utilization (efficiency) than Non-Posted type.
So why should it be divided into Non-Posted and Posted? For Memory Writers, the requirement for efficiency is high, so Posted is used. However, this does not mean that the Posted type operation does not require the Completer to answer, but at this point the Completer adopts another response mechanism, the Ack/Nak mechanism.
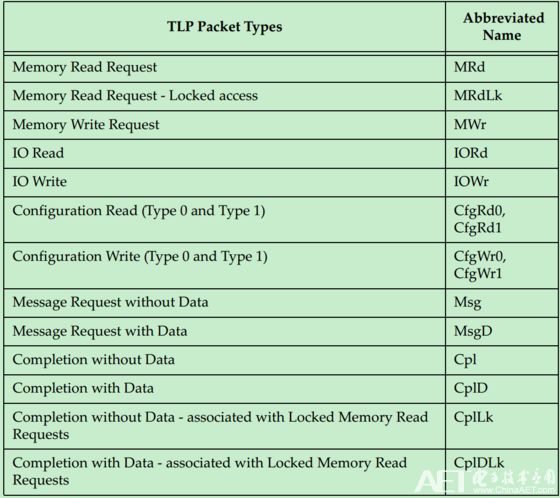
There are several types of PCIe TLP packages:
A schematic diagram of the TLP transmission is shown below:
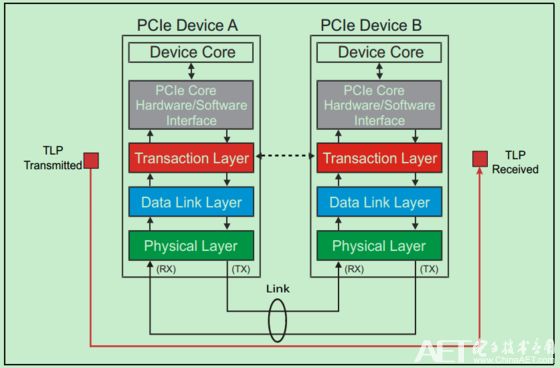
The location of the TLP in the entire PCIe packet structure is shown in the following two figures: (The first one is the sending end and the second one is the receiving end)
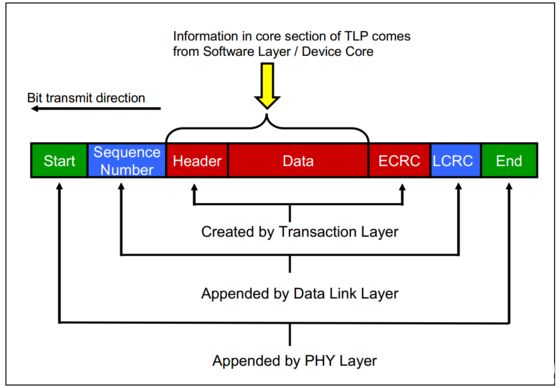
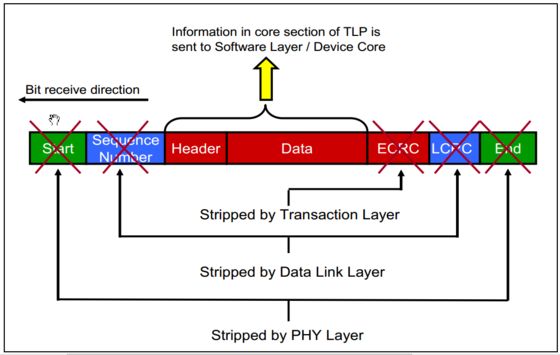
Among them, the structure diagram of TLP package is shown as follows:
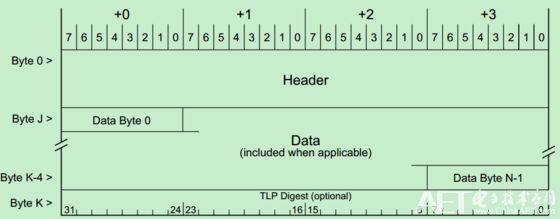
The TLP Digest in the figure, End-to-End CRC, is optional. In addition, the length of the TLP (including Header, Data, and ECRC therein) is in units of DW (double word, ie, four bytes).
Insulated Power Cable,Bimetallic Crimp Lugs Cable,Pvc Copper Cable,Cable With Copper Tube Terminal
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperterminals.com