There are currently three main image stabilization methods used in mobile, consumer, and automotive applications, including digital image stabilization (DIS), electronic image stabilization (EIS), and optical image stabilization (OIS). The main difference between DIS and EIS is the motion detection method. DIS uses a pixel mapping method, as shown in Figure 1. The DIS method places the dog in the middle by analyzing the picture. In other words, the pixel mapping method uses software to readjust the dog's position.
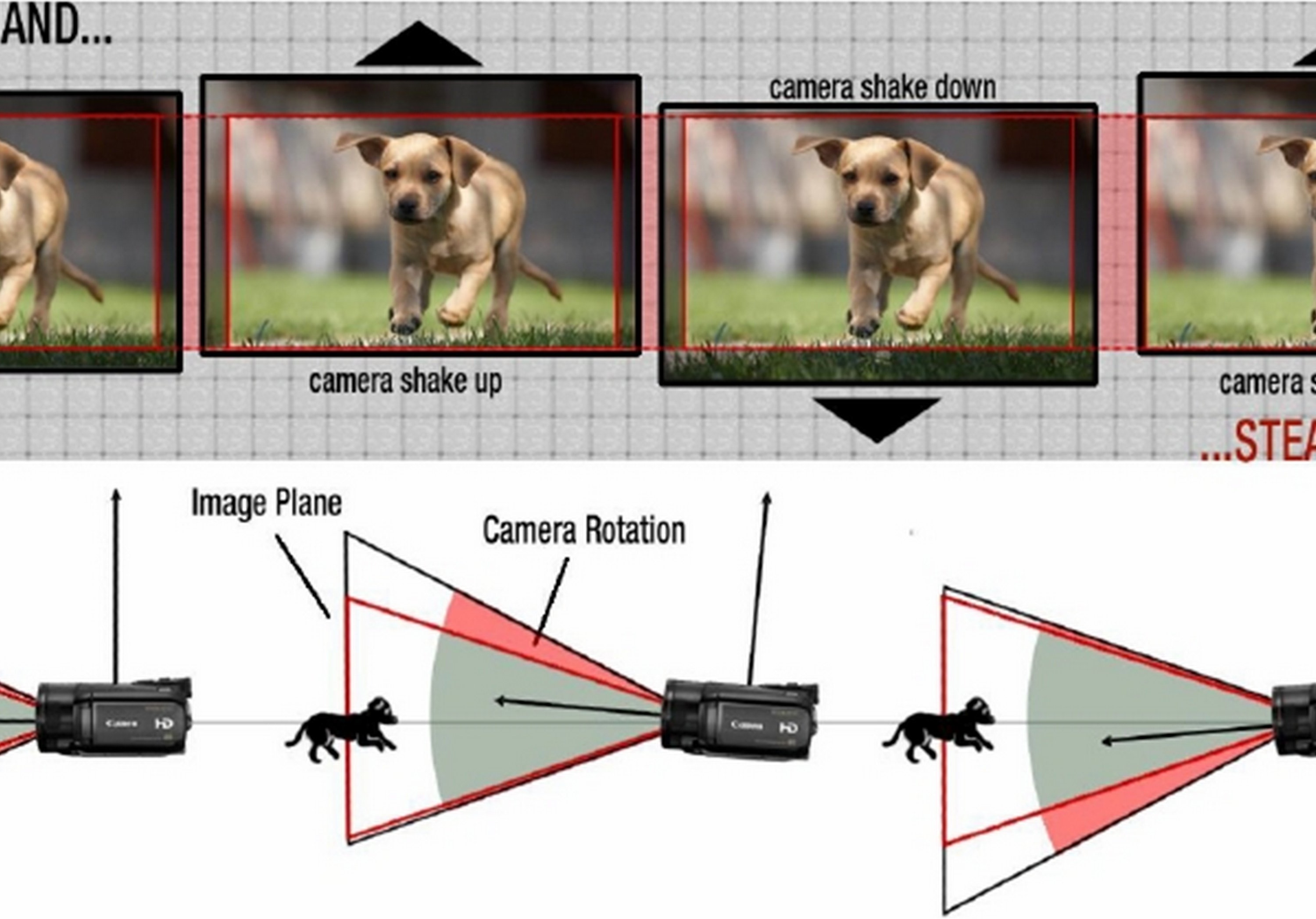
Figure 1. Digital image stabilization (DIS) uses a pixel mapping method to stabilize the image through software.
In comparison, EIS uses a gyroscope to detect camera motion and compensate for motion in real time, improving pixel and image quality to the highest. Both methods provide motion compensation by cropping the image. Since EIS uses a gyroscope to sense motion, EIS sensing accuracy is excellent, but because it still relies on cropping the image for motion compensation, the image quality is degraded. In Figure 2, you can see how the guard band is used to crop the image to compensate for jitter.
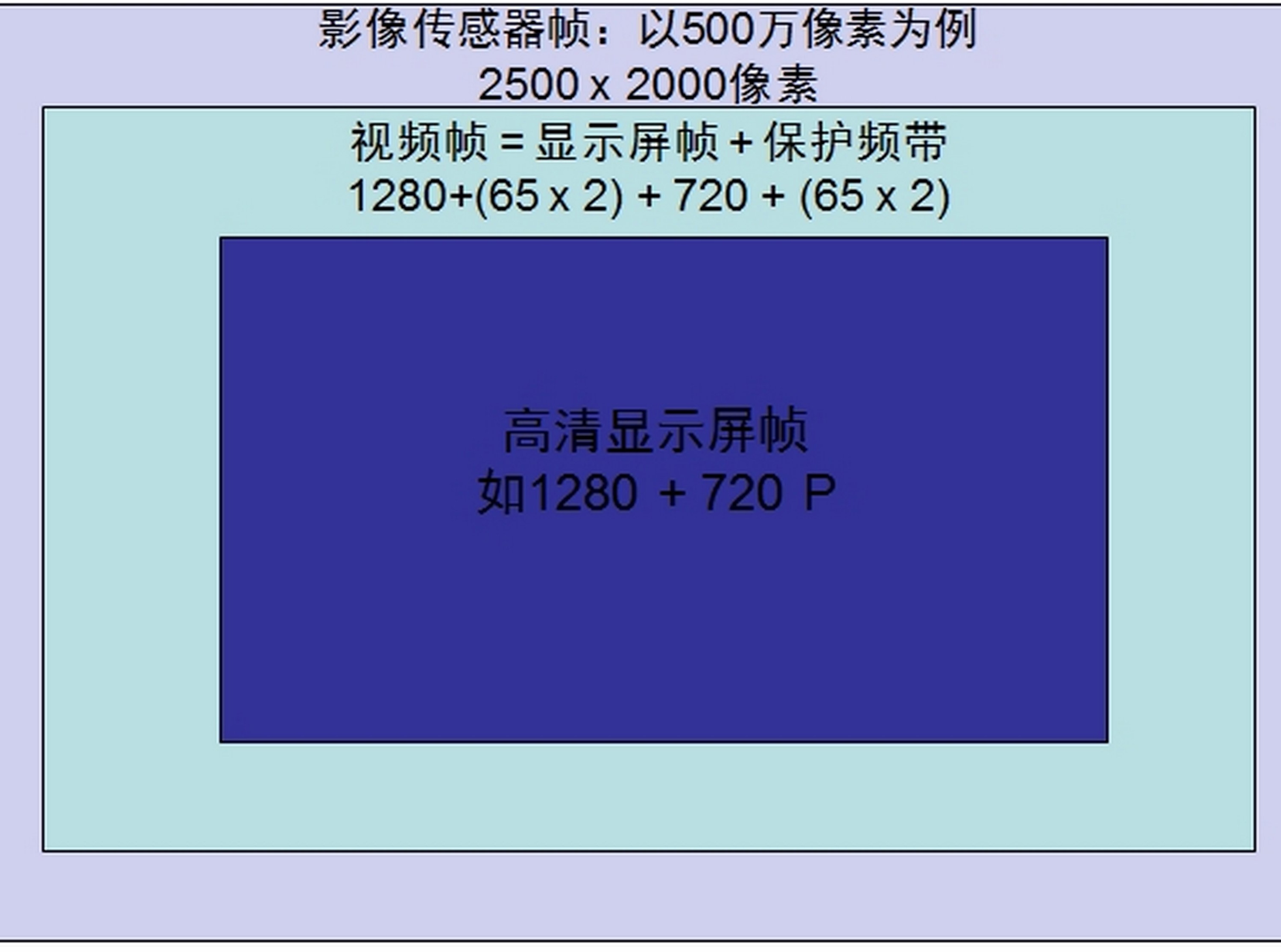
Figure 2. Electronic Image Stabilization (EIS) uses a gyroscope to detect camera motion and compensate.
Most applications use an application processor (AP) to process video or signals, including applications that use EIS and DIS. Especially DIS requires more processor resources to compensate for jitter and motion. In video applications, video compression is equivalent to image quality. When methods such as DIS and EIS require cropping, the quality of the image will decline, because the quality of the captured image must be continuously reduced and improved.
In comparison, the OIS method captures and uses the largest pixels, and does not need to reduce / improve the image quality through the guard band, so it provides maximum compression and optimizes the image quality. And because OIS provides internal compensation, it does not require any other application processor resources.
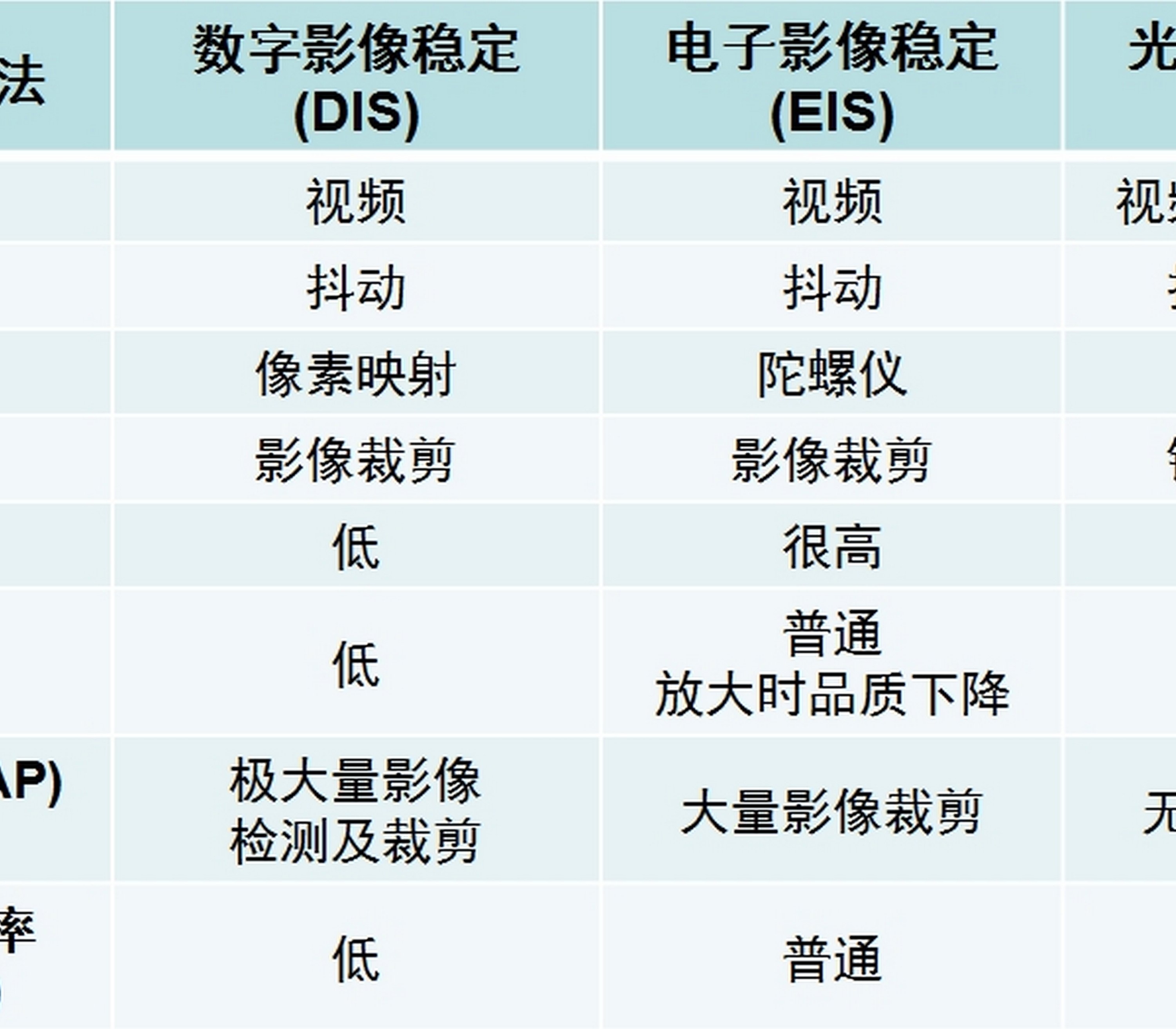
Table 1. Comparison of various image stabilization methods.
Other advantages of the OIS method
In addition, the unique OIS method also provides a greatly improved shutter speed and optimized exposure compensation up to 3 levels, much higher than other methods used. The OIS scheme usually consists of some major components, including an image sensor to determine the focal length, a gyroscope to compensate for motion, and optical image stabilization. These components can be assembled in a small space, using some standard design wiring.
OIS usually also integrates an open-loop or closed-loop autofocus design. Open-loop autofocus uses springs to provide resistance to lens stretching, and requires continuous power to resist lens stretching and keep it in position. By using a closed-loop autofocus system, you do n’t need a spring and continuous power to maintain the autofocus lens position. Since the position is known, less power is required to maintain the focus of the application. In a closed-loop AF system, the related power required in macro mode is no more than infinity. This also has a significant impact on the settling time required by each system. Because the typical open-loop AF takes time to stabilize, and then you have to continue to re-adjust. The time depends on the algorithm used, but it usually takes some time for the open-loop AF to stabilize. The closed-loop autofocus system uses a position sensor to determine the lens position, which can speed up the stabilization time to complete focusing.
Commonly used for longitudinal water blocking include water blocking yarn, water blocking powder, and water blocking tape
Dongguan Bofan technology Co., LTD , https://www.ufriendcc.com