Many new HAMs were very active after buying the call sign. They bought a hand trolley and were ready to connect with the local repeater to make more ham friends. However, they often encountered a problem, obviously their frequency and relay. The frequency of the station is on, why can no one respond to the launch anyway? It turned out that the subsonic frequency difference frequency is not set correctly. So what is the frequency of subsonic and frequency difference? This article will answer for you.
1. Offset frequency (Offset)
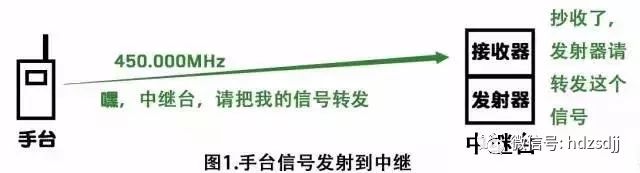
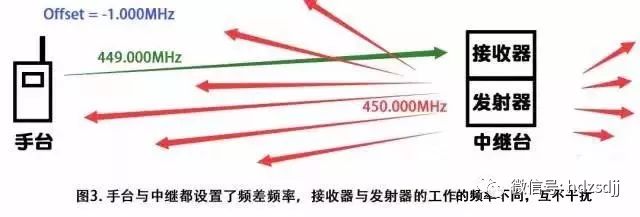
Frequency difference frequency refers to the frequency difference between radio transmission and reception. For example, the transmission rate of a radio station is 450 MHz and the transmission frequency is 449 MHz. Then the frequency difference of this station is 1 MHz, and the frequency difference is recorded. for
"-1.000MHz"
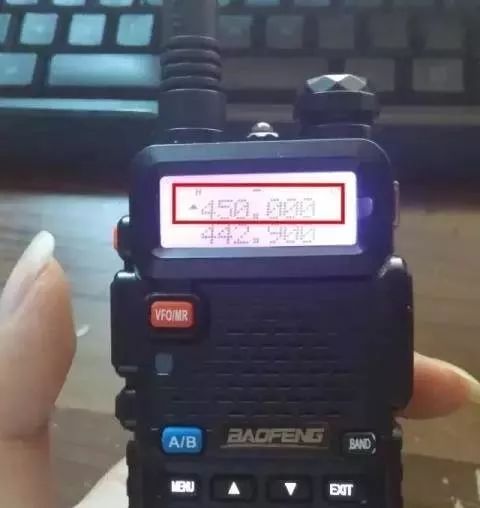

The radio receives a frequency of 450.000 MHz
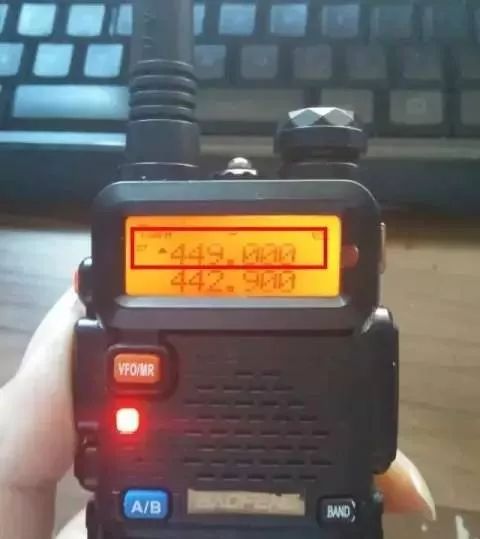

The frequency is 449.000MHz when transmitting

The radio frequency difference of this radio is set to -001.000MHz
So the transmit frequency is 1MHz lower than the receive frequency
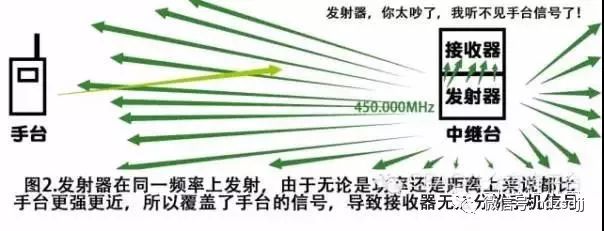
The role of the frequency difference frequency is to avoid the frequency conflict between the receiving station and the transmitting station. The relay station works by relaying your signal while receiving the signal you transmitted in the past, so if the receiving and transmitting are using the same frequency, the repeater will not be able to identify the signal you are sending and the signal it has transmitted. normal work.
2. Private tone
Subsonic is a kind of special frequency that is loaded on the sound signal. It acts like a signal identity card. The signal is marked so that other stations or repeaters can distinguish whether this signal needs to be received.
The most commonly used subtone is CTCSS (Continuous Tone Coded Squelch System). Direct translation is a continuous audio coding squelch system. Motorola calls it PL. It is an analog subsonic frequency ranging from 67.0Hz, 69.3Hz, to 250.3Hz. 39 subtones (or 50 points). When transmitting, this low-frequency unaudible signal (hence called subsonic) is continuously superimposed on the frequency and transmitted, and the other party only receives such same frequency to receive it, for anti-interference, or not to listen to signals that are not for themselves. .


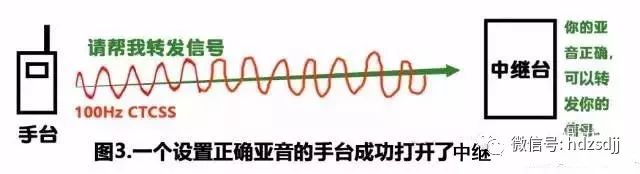
The subtones transmit subtones and receive subtones. In general, in order to be able to relay, all transmit tones are used so that the relay can be opened. The relay itself adopts "receiving subsonic", and signals without subsonic signals are rejected. Some of the relayed signals are not subsonic but are also subtone.
Similarly, in order to reject signals that do not need to be heard, they can also receive the same subtone when they receive them. In this way, an agreed-upon tone can also be used between two stations (or several stations) to exclude external interference signals.
Although it is a subsonic sound, it can actually be heard, especially if the subsonic sound is set at a high limit (around 250 Hz), or when the receiver's low frequency response is good. Therefore, when we set up subtones, we try to set them as low as possible to avoid unnecessary interference.
In addition, there is a subsonic DCS (Digital Coded Squelch), which is a digital subsonic, Motorola is called a DPL, there are 104 subtones (less DPL), more advanced, and is digitally encoded before speech and before the end of transmission. Form emission. This type of subsonic can only be transmitted and received at the same time (ie, it cannot be set to transmit but not receive).
Newbie misunderstanding:
Q: When transmitting subtones, the receiver can only receive sub audio receivers.
A: wrong! In fact the opposite is true. When transmitting subtones, the receiving party is set to receive a “non-subaudible reception stateâ€, and when it is set to “subaudible reception stateâ€, the subtone type must be the same and the subtone code must be the same to receive.
Draw-wire sensors of the wire sensor series measure with high linearity across the entire measuring range and are used for distance and position measurements of 100mm up to 20,000mm. Draw-wire sensors from LANDER are ideal for integration and subsequent assembly in serial OEM applications, e.g., in medical devices, lifts, conveyors and automotive engineering.
Linear Encoder,Digital Linear Encoder,Draw Wire Sensor,1500Mm Linear Encoder
Jilin Lander Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jllandertech.com