The term short-range wireless device covers wireless transceivers that enable one-way or two-way communication without interfering with other wireless devices. SRDs are widely used and offer a wide range of services. Popular applications are: remote control applications in home or building automation systems, wireless sensor systems, alarms, cars (including remote keyless door locks and remote car start), and voice and Wireless transmission of video Wireless system designers of short-range wireless devices must be very careful when selecting wireless communication frequencies. In most cases, the selectable frequency range is limited to the unlicensed band, provided that certain specifications and conditions of use are met. Table 1 lists the available frequency bands for short-range wireless devices worldwide.
When designing a global system, designers typically use the 2.4 GHz band. In fact, 2.4GHz has become the preferred operating frequency band for standards such as Bluetooth, WLAN and ZigBee. In wireless phones or 802.11a versions of WLAN applications, the 5.8 GHz band also occupies some status.
However, for systems that require longer transmission distances and lower power consumption, the frequency bands below 1 GHz are attracting attention due to fewer coexistence problems and longer transmission distances, because both of these performances affect power consumption. Power consumption is an important consideration in battery-powered applications.
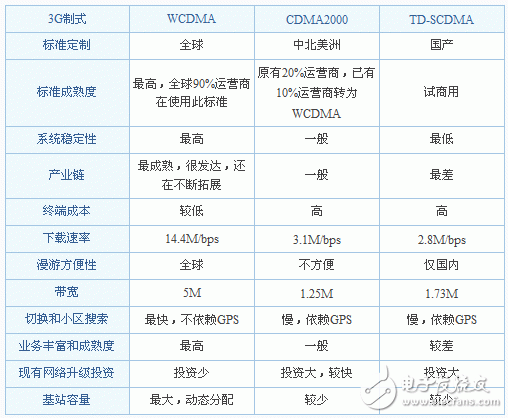
WCDMA is a third-generation mobile communication system based on the GSM MAP core network and UTRAN (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network) as a wireless interface. It evolved from Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) and is officially considered a direct extension of IMT-2000, which provides higher mobility for mobile and portable wireless devices than is currently available on the market. Data rate. WCDMA uses direct sequence spread spectrum code division multiple access (DS-CDMA) and frequency division duplex (FDD), and the chip rate is 3.84 Mbps. W-CDMA can support voice, image, data and video communication between mobile/handheld devices at rates up to 2 Mb/s (for local area networks) or 384 Kb/s (for broadband networks). The input signal is first digitized and then transmitted in a coded spread spectrum mode over a wide spectral range. Narrowband CDMA uses a carrier frequency of 200KHz width, while W-CDMA uses a carrier frequency of 5MHz width. Currently, WCDMA licenses are allocated to China Unicom.
CDMA2000, CDMA2000 1&TImes; EV, is a 3G mobile communication standard. There are two phases: CDMA2000 1&TImes; EV-DO (Data Only), which uses voice-separated channels to transmit data, and CDMA2000 1&TImes; EV-DV (Date and Voice), that is, the data channel is unified in the voice channel. CDMA2000, also known as CDMA MulTI-Carrier, was led by Qualcomm North America, and Motorola, Lucent and later Samsung joined South Korea. Korea is now the leader of the standard. The system is derived from the narrowband CDMA One digital standard and can be upgraded directly from the original CDMA One architecture to 3G with low construction costs.
TD-SCDMA is the abbreviation of Time Division-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access, which is one of the three 3G standards approved by the ITU, compared to the other two major 3G standards (CDMA2000) or WCDMA) It started late. TD-SCDMA is also the only 3G standard developed by China. The standard incorporates technologies such as smart antennas, synchronous CDMA, and software-defined radio (SDR). With time division duplexing, the uplink and downlink channel characteristics are basically the same. In addition, the use of smart antenna technology in TD-SCDMA has inherent advantages, and the use of smart antenna technology introduces the advantages of SDMA, which can reduce interference between users and improve spectrum utilization. TD-SCDMA also has the advantage of TDMA. It can flexibly set the ratio of uplink and downlink time slots and adjust the ratio of uplink and downlink data rates. It is especially suitable for occasions where there is less uplink data and more downlink data in Internet services. However, the variability of such uplink and downlink switching points adds a certain complexity to the same frequency networking.
Multi-Function Electric Blender
Multi-Function Electric Blender,High Speed Blender,Heating Cooking Blender,Cooking Blender For Home
Shandong Sangle Group Co.,Ltd. , https://www.sangle-group.com