1. High voltage flash circuit
The high-voltage flash lamp generates a high voltage through the oscillating circuit and the step-up transformer. The large capacitor stores energy, releases and induces a high voltage at a required moment, and excites the inert gas to emit a pulse light source, thereby obtaining extremely strong instantaneous power. Figure 1 is a prototype of a flash lamp consisting of a helium-filled glass cover with its negative and positive electrodes all immersed in helium and the trigger pole connected to the lamp surface without being immersed in helium.
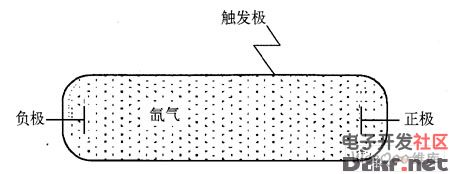
Figure 1 Prototype of the flash
When the impedance of the helium gas drops to a very low value, a strong current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, producing a strong visible light. This is done by the trigger pole, which produces a very high peak voltage (several kilovolts), which causes the helium to be ionized and enter a low impedance state. At present, most commonly used flash circuits are high-voltage flash circuits, which are composed of an oscillating circuit, a step-up transformer, a large energy storage capacitor, a high voltage coil, and an inert gas flash lamp. A typical circuit diagram is shown in FIG.

Figure 2 Typical high voltage flash circuit diagram
The output of the flash is very light and has a wide coverage. The color temperature of the flash is about 5500 ~ 6000K, very close to the color temperature of natural light, so no color correction is required. In addition, because the output light requires very high electrical energy (a few hundred volts is required on the anode), it takes some time to raise the battery voltage to the voltage required by the flash.
Under normal circumstances, the interval between two consecutive flashes is between 1 and 5 s. The length of time depends on the input power, capacitance, charging circuit characteristics and required power. The flash can only be pulsed, so it is a good camera-assisted light source solution, but not suitable for moving images.
In addition, Xenon flash tubes and their associated drive electronics take up a lot of space, and mobile phones have limited space available. And because igniting helium, providing the right energy, and ensuring that the light output requires a high voltage requires an accurate and costly drive, these factors limit the use of high-voltage flashlights on mobile phones.
SHENZHEN CHONDEKUAI TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD , https://www.szfourinone.com