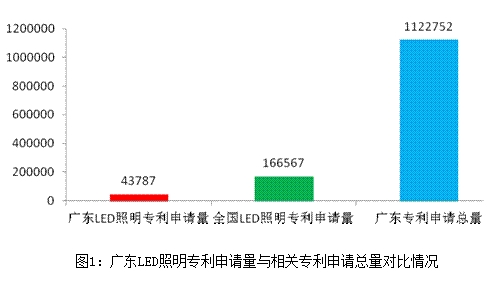
 In recent years, under the vigorous advocacy and support of governments at all levels in Guangdong Province, it has rapidly developed into an area with the largest industrial scale, the strongest industrial agglomeration ability, and the most complete industrial chain. However, there are still outstanding problems such as weak technical foundation and large patent risks, which have become an important bottleneck restricting the sustainable and rapid development of the industry.
In recent years, under the vigorous advocacy and support of governments at all levels in Guangdong Province, it has rapidly developed into an area with the largest industrial scale, the strongest industrial agglomeration ability, and the most complete industrial chain. However, there are still outstanding problems such as weak technical foundation and large patent risks, which have become an important bottleneck restricting the sustainable and rapid development of the industry. First, Guangdong LED lighting industry's overall patent applications <br> <br> the end of June 2013, Guangdong LED lighting industry, a total of 43,787 patents, accounting for 26.29% LED lighting industry, the national patent, patent applications accounted for Guangdong Province 3.90% of the total.
From the perspective of the structure of patent applications, as of the end of June 2013, Guangdong Province's LED lighting industry applied for 9,684 invention patents, accounting for 22.12%; utility model patents, 24,573, accounting for 56.12%; design patents, 9,530, accounting for 21.76%.
Second, around the city of Guangdong LED lighting industry patent application <br> <br> situation from the point of view of the geographical structure of patent applications, nine municipalities in the Pearl River Delta, Guangdong Province, 93.42% of the total LED lighting patent applications accounted for the remaining cities only 6.58%. In the Pearl River Delta nine cities, there are seven patent applications for LED lighting, including Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Zhongshan, Foshan, Huizhou, and Jiangmen. Shenzhen has 17 patent applications and ranks first in the province, accounting for the province’s patents. Nearly 40% of total applications.
Of the seven prefectures where LED lighting applications in the province exceeded 1,000, the ranking of invention patents was: Shenzhen (5755), Guangzhou (1322), Dongguan (935), Zhongshan (479), Foshan ( 413), Huizhou (206), Jiangmen (170), the highest proportion of Shenzhen, accounting for 33.13%, followed by Guangzhou, accounting for 24.37%, the lowest proportion is Zhongshan, only 10.33%.
Among the provinces where LED lighting applications for patents exceeded 1,000, the number of utility model patents was ranked as follows: Shenzhen (9323), Dongguan (4366), Guangzhou (2927), Zhongshan (2286), and Foshan (1808). Parts), Huizhou (783 pieces), Jiangmen (601 pieces). Of the three types of patents, utility model patents are the highest percentage of patent applications for LED lighting applications in various cities in Guangdong. Of the above seven cities, utility model patents accounted for the highest proportion of LED lighting patent applications in total, accounting for 66%, followed by Foshan, accounting for 58.14%, the lowest proportion is Zhongshan, utility model patents accounted for the total number of LED lighting patent applications 49.32%.
Among the provinces where LED lighting applications in the province exceeded 1,000, the design patent ranks as follows: Shenzhen (2295), Zhongshan (1870), Dongguan (1314), Guangzhou (1175), Foshan (889) ), Huizhou (513), Jiangmen (338). Among the seven major cities, design patents accounted for the highest percentage of patent applications for LED lighting in Zhongshan, accounting for 40.35%, followed by Huizhou, accounting for 34.15%, and Shenzhen, accounting for only 13.21% of the total.
Third, the current Guangdong LED companies are facing the main risks of patents (a) patent barriers of multinational companies Currently, the LED industry a large number of core patents still in Japan, Asia, Japan, Kerui, Germany Osram and other international giants, the formation of patent barriers. For example, as one of the most advanced LED lighting technologies in the world and one of the most patented technologies, Philips has granted patents for Philips LED system technology and solutions to the 300 companies since May 2012 through the launch of the "LED Licensing Program." In combination, three LED lighting companies in China have joined the plan. For companies that refused to join the program, Philips appealed to the law by means of legal means. For example, Philips sued Nexxus Lighting for patent infringement. Both of them finally reached a licensing agreement. Philips may use it in combination with threats and lawsuits for Chinese LED companies. And domestic OEM factories. Although the specific details of patent licensing fees are still not clear, Philips' patent licensing will obviously increase the production costs of domestic LED companies, especially for OEM foundry companies. Most of the profits will be used to pay for patent licensing fees.
(II) Risks arising from the formation of patent alliances by large foreign companies Currently, international large companies have formed a cross-license agreement, such as Nichia, Philips, Cree, Toyota Synthesizer, OSRAM, etc., to reach a wide range of patent cross-licensing agreements. A patent coalition in a sense. LED industry in Guangdong concentrates on the packaging and application of downstream industries. It is dominated by small and medium-sized enterprises. The industrial development time is short, the number of patents is small and the technological strength is backward. It is impossible to obtain equal bargaining rights. It is isolated from the core patent license and is easily patented. The league's suppression goals. In the future, these international giants are likely to target the majority of SMEs, possibly as the communications industry moves toward standardization to obtain higher licensing fees. Strong enterprises should be encouraged to enter into patent cross-licensing agreements with national manufacturers on the basis of independent intellectual property rights, and enter these patent union adaptation rules, gaining the right to participate and speak in the international market, standard setting, and patent technology development trends. . At the same time, due to the high cost of patent litigation, lengthy litigation time, and complicated procedures, enterprises are often struggling to cope with, and lawsuit confidence is not enough to rush to reach reconciliation and pay licensing fees.
(III) Intellectual property risks of OEM companies The LED industry of Guangdong Province gathers a large number of small and medium-sized private enterprises that operate as OEMs. They lack the funds and talent needed for independent innovation, and their awareness of intellectual property rights is weak. They pay more attention to orders from foreign countries. , cost, delivery time and other traditional international trade factors, such as the Hongxing company entrusted with Foshan Gaobao Lighting Co., Ltd. to produce and process tungsten halogen lamps for motor vehicles in 2004. Although Hongxing required relevant laws and regulations in China, foreign companies are required to show relevant knowledge. The title certificate, but it had not been subject to substantive examination, was finally found to have infringed the trademark right at the customs and the goods were confiscated and fined. Even OEM companies can not be exempted from the responsibility for patent infringement even if they produce according to the demand side's technical drawings and sample OEM. The behavior of OEM OEM production is the “implementation patent†constitutes patent infringement, because the main technology involved in providing products by OEM manufacturers. OEMs will have to bear the main responsibility for the intellectual property rights of their products. At the same time, the international LED lighting giant through the technological innovation, patent applications, the development of standards, quality standards, with our country's sound industrial support, human resources, industrial policy, commissioned by OEM companies OEM production, such as Philips in Shenzhen, Dongguan, Zhongshan commissioned more Home factory OEM production. In addition, more small and medium-sized OEM companies directly accept orders from foreign distributors for OEM processing, and there are dual risks of trademark infringement and patent infringement.
(IV) LED brand construction and trademark infringement risk From the perspective of the entire LED industry, China is still in the initial stage of brand cultivation, lacks well-known brands or well-known trademarks, and there is a risk of trademark infringement. On the one hand, there are trademark infringements such as “copying†of registered trademarks, “free riders†and “rubbing the ballâ€, such as the NVC lighting brand, products found on the market bearing the “Leishi†and “NVC Cardin†trademarks. In 2012, OSRAM sued the self-employed who registered the “Okron†trademark. On the other hand, the trademarks of Chinese companies also have the risk of being registered by foreign companies. For example, the Xiamen Donglin “Firefly†brand was rated as the top ten famous brands in the lighting industry in China, but the “firefly†trademark was Siemens and OSRAM in the international market. The company has registered in 18 countries in Europe. While our enterprises are concerned about avoiding infringement of the rights of others, they must also gradually turn to legal weapons to protect their own intellectual property rights.
Since the fourth, Guangdong LED industry to deal with intellectual property risk countermeasures <br> <br> enter 2013, China's LED market has been showing good development trend gradually, to promote the rapid and healthy development of Guangdong LED industry, governments, businesses should have the appropriate The intellectual property risk response policy:
1. The government should speed up the development of LED industry IP strategies at the regional level Although international giants have built up intellectual property barriers, manufacturers with core technologies are making high profits through the patent network. However, unlike other industries, because of the long LED industry chain, a variety of technical routes, and a wide range of applications, companies that are at a disadvantage in patent competition can bypass existing patent barriers through different technical routes, or combine existing technologies. The industrial base forms its own characteristic technical field. Therefore, Guangdong has integrated its national science and technology development plan and established its own intellectual property strategy as a strategic guideline for the development of the local LED industry.
2. The industry should speed up the promotion of intellectual property management standards This year, the state has issued the "Enterprise Intellectual Property Management Standards," which is China's first national standard for corporate intellectual property management. This standard takes the enterprise's intellectual property management system as the object of standardization. It aims to guide enterprises in establishing a scientific, systematic and standardized intellectual property management system, helping enterprises fully implement the spirit of intellectual property strategy, actively responding to the competitive situation of intellectual property, and effectively improving intellectual property rights for enterprises. The level of contribution to business development. In this regard, the LED industry should promptly implement and implement the “Enterprise Intellectual Property Management Standards†standard, implement a standardization strategy, and improve the company’s intellectual property management level.
3. Accelerate the establishment of the LED industry patent alliance.
With the acceleration of technology renewal, Guangdong enterprises have become more and more intensive in the fields of downstream packaging and application of barrier patents and complementary patents, making it impossible for enterprises to fully and effectively use these patented resources. A large number of potentially valuable patents are idle and repeatedly developed. The phenomenon is more serious, and no one company has the strength to independently compete with international multinationals in the weak upstream epitaxial chip technology. In order to respond to the patent blockade of foreign giants multinational corporations, to accelerate the establishment of the LED industry patent alliance for the development status of the LED industry in the province, through the establishment of a patent alliance, a patent or complementary patent for a certain technology can be jointly and uniformly licensed. Eliminating the barriers to cross-licensing of this technology will not only allow licensees to independently negotiate lengthy patent licenses with each member of the patent union, but also greatly save the time and costs of both parties to the transaction, and promote the development of the regional LED industry.
Replacement Bulb Lamp With Housing
Replacement Projector Lamp with housing has one more case than the bare bulb lamp, which can be directly put into the projector and more convenient than the installation of the bare bulblamp. The projection effect is the same as the compatible projector lamp, with stable light source and brightness, which can support daily life use
Replacement Bulb Lamp With Housing,Bulb Lamp,Dynamic Projector Lamp,Led Projector Lamp
Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.happybateprojectors.com