
With the advancement of eye tracking technology, augmented reality and virtual reality technology (hereinafter referred to as AR/VR) are achieving a greater technological leap. According to Memes Consulting, in recent years, AR/VR has grown rapidly with the support of many start-ups and technology giants such as Google, Apple, Samsung and Facebook. Although a lot of experience has been accumulated, the hardware of AR/VR is still in a relatively "extensive" stage. Most interfaces get information through head movements and handle input. The graphics/images are not real, and eye damage is also increased due to reduced decision making and decreased fitness. The eye tracking system can monitor eye activity in real time, so it may change the status quo of hardware backwardness. From a traditional perspective, this technology has been used for scientific and commercial purposes to gather information for market analysis and medical diagnosis. Since humans mainly use vision to perceive the surrounding environment, the eyes can reveal their thoughts. The eye tracking system can inform the device: the user's strengths and coping styles. In terms of processing information, eye tracking allows one device to communicate with another device without a handle input, without a corresponding button, without a controller, and without a mouse, which can be a "human-machine relationship". The foundation of the revolution. For example, a smartphone or Laptop for eye tracking and verbal commands can use human thinking to perform many other activities compared to devices that use only a mouse or keyboard to communicate. Network issues (Internet of Things (IoT)) and the development of unmanned and smart homes depend on the development of such human-machine relationships. With small, highly efficient devices and compact infrared light-emitting diodes (IREDs), companies are finally integrating eye tracking sensors. Such systems may allow virtual displays to respond to natural, even unintended, user prompts when performing efficient operations. This will be the beginning of a truly immersive virtual experience. The industry is changing. In January 2017, Japan's VR startup FOVE launched a primary eye tracking VR headset.

At the same time, some mid- to high-end AR/VR hardware companies have been working hard to add eye tracking to existing headsets, and these headsets will appear sooner or later, in addition to built-in options. Tobii and various eye tracking manufacturers have also begun to license their customers' AR/VR equipment expertise, while technology giants such as Google and Facebook have acquired some of the most promising startups in the field. As customer enthusiasm continues to climb, AR/VR products have had a profound impact in the market. According to Parks and Associates, 9% of Internet homes, including the US, expect to purchase VR headsets in the following year, and 24 million families worldwide will achieve this by 2017. According to UBI Analysis, global shipments will exceed 65 million units by 2021. International Data Corporation (IDC) expects AR/VR headsets to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 108.3% over the next five years. According to data from Bloomberg Expertise, VR/AR sales will reach $8.5 billion in China alone in the next four years. At the same time, Market Watch believes that by 2023, the attention monitoring market will reach a market size of 1.4 billion US dollars due to its role in VR/AR products. How Eye Tracking Supports People's Immersive Experience The long-term goal of AR/VR is to be completely immersed – an ability to pull users from the real world into the virtual world without interruption. This is one of the most advanced careers in the history of modern information technology. To achieve this illusion, the hardware will get rid of the handle input and let the user work in the virtual world as if it were a real world. It takes time to reach this stage of technology. Here's how eye tracking promotes immersive options: visual rendering We can see the visible details of objects in our center of view through the central fossa of the retina (most sensitive to visible light, at the bottom of the retina, behind the pupil). The change of objects in the fovea appears to be vague. This way, like most AR/VR systems, using the same decisions will ultimately be a waste. Visual rendering is a digital imaging process that simulates the state of our viewing: by reducing the effects of the environment, the target of the fovea is displayed in high resolution. Because attention is constantly changing on the display, eye tracking is important to find the point of attention. This technology is quite gentle on the eyes and hardware. Visual rendering greatly reduces load and power consumption by reducing the reliance on total pixels without changing picture integrity. This frees up resources that can be reused for other operations that enhance their value. Because of this, users experience much less delay and exercise illness, and the stability of the display is improved. The Eye Tribe's video demo recorded significant improvements to the system benchmark, including: graphics processing unit (GPU) load reduced from 80-90% to 40-30%; clock frequency reduced from 1200 MHz to 800 MHz; thermal design Consumption (TDP) has dropped from 70% to 40%. Precise pupil distance (IPD) users interact with AR/VR technology through a set of lenses called “gogglesâ€. “These lenses should be consistent with the user's pupils to fully display the three-dimensional space.†If not aligned, the attention is impaired and the image becomes flat and blurred.

Finding the right location is difficult. The distance between the pupil center points is called the pupil distance (IPD), and the adult's IPD range is between 5.1 cm and 7.7 cm. This change is evident when using binoculars, microscopes, and telescopes, and the IPD needs to be adjusted to fit the user for the best detail and depth. Most AR/VR headsets are compensated for by using larger goggles or handles. With the eye tracking system, the pupil position can be found inside the device, and the new product can accurately calculate the IPD. The best match allows the user's eyes to relax and achieve full interaction in the experience, thus improving the overall real display. Natural user interface (UI) When the display responds to eye movements, not just head positioning, the user gains a more natural view. Eye tracking allows the user to select only virtual objects, such as balls or weapons in motion, or to new locations in the virtual environment. This can avoid the appearance of cumbersome icons on the display and reduce the psychological resources occupied by navigation. In augmented reality, the direct gaze interface may allow users to pick out purchases in physical retailers without the help of a staff member. The social reaction eye is the first tool for our communication. Before we speak, we can feel the emotions through subtle facial expressions. By tracking eye changes, immersive hardware helps software packages identify and respond to users with greater sensitivity. These expertise can help avatars to behave by giving them insight into social cues. The new virtual character delivers the eye movements of human opponents, bringing new dimensions to video games and different virtual content materials. Seamlessly identifying a person's iris is as unique as its thumb fingerprint. Eye tracking is performed by iris scanning, and the AR/VR headset can make the access system easier and safer without a password.

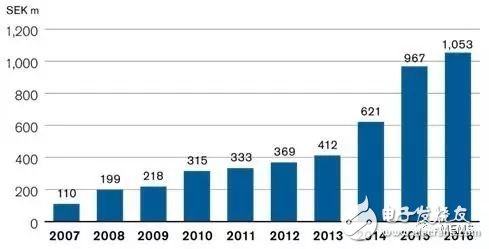
After major breakthroughs in eye movement monitoring and innovation , the development of applied science with significant influence tends to accelerate. Today, FOVE has released a primary eye tracking VR headset, and we anticipate that these features will soon be widely used in a range of products – from inexpensive smartphone headsets to high-end systems. Oscar Werner, President of Tobii Business Unit, explained to TechCrunch: "Eye tracking will be an important part of the second generation of headsets. This view has been supported by a large number of VRHMD suppliers. This will promote the development and innovation of professional technology." References, shortly after Tobii began investing in VR technology, its total sales almost doubled from 2014 to 2016.
To take advantage of this volatile market, hardware manufacturers may want to keep eye tracking systems in line with the human eye. This technical principle can gently illuminate the cornea with invisible infrared (IR). Light is transmitted through the pupil without being noticed, and the edge of the pupil is displayed on the camera sensor. An eye twitch called "sweeping" is one of the fastest movements in the human body - the eye can move 0.9 degrees / millisecond and trigger motion within 200 milliseconds. The use of attention monitoring systems in AR/VR should match this speed, especially in the visual rendering function where the position of the image should be modified per eye movement. In addition to high-efficiency memory cards and small fine-tuning sensors, eye tracking requires an environmentally friendly, lightweight, and gentle infrared source. Based on this function, OSRAM Opto Semiconductors developed the Firefly FH 4055, an IRED for close-up eye tracking (the distance between the attention and the sensor is less than 5 cm). The Firefly FH 4055 is mounted sideways for maximum reflection and minimum power consumption.

Eye tracking provides AR/VR developers with a unique opportunity to have an opportunity to interact with human minds. With the advancement of professional technology, ultra-small infrared emitters play an important role in hardware innovation. Further reading: "Samsung Galaxy S8 Iris Recognition System" "Infrared LED and Laser Technology, Applications and Industry Trends" "HTC Vive Virtual Reality (VR) Head-mounted Display" "Oculus Rift Virtual Reality (VR) Head-mounted Display Device"
Windows Tablet
C&Q Technology (Guangzhou) Co.,Ltd. , https://www.gzcqteq.com