Infrared thermal imaging equipment is gradually heating up. If you still think that the thermal imager is a high-end professional equipment, it is a military equipment. It is still far away from us. Sorry, you are out! The thermal imager we have in mind often appears in specialized operations such as military investigations and navigation operations. Today, the application of thermal imaging cameras is almost everywhere. In recent years, with the development and popularization of handheld infrared cameras, military professional precision instruments have gradually transformed into portable, intelligent, and even civilian popular products with Wi-Fi/cloud thermal imaging. If you are worried about leaking water, leaking mobile phones or TV screens, or inflammation in your body, you can be pleasantly surprised to tell you: handheld cameras can solve such problems in one stop. Upload the cloud for storage and big data management. Similarly, many industries are changing due to the popularity of thermal imaging cameras: for example, if a firefighter has a handheld thermal imager, it can accurately determine the location of the fire point and accurately locate the trapped person; for example, an earthquake When it happens, if the drone has a thermal imager, it can rush through the obstacles in the first time, find out the situation in the disaster area, and immediately find the trapped people, and will not reproduce the former rescue workers. The situation of the road, delaying the best rescue time; for example, as small as an ordinary store or family, as large as the country, the security system can accurately determine whether there are unsafe factors by using a thermal imager; for example, the process of producing and processing products In the test, many of them are invisible to the naked eye and the accuracy of the ordinary instruments is limited. If there is a thermal imager, all the problems will be "clear at a glance". The application of thermal imaging cameras is now available in every corner of our lives, from common medical imaging to spectral detection around us, from the gradual understanding of food detection to military radar modeling, from the most familiar safety on a daily basis. Check out the upcoming autonomous driving and smart life.

FLUKE Visual Infrared Thermometer VT02 is an inspection tool for electricians and maintenance technicians . Industrial application scenarios of infrared thermal imaging cameras. Perhaps you are not familiar with the industrial application of thermal imaging cameras. The following is a brief introduction to thermal imaging cameras in industrial automation. Applications: Thermal imaging cameras play an irreplaceable role in five applications: automated inspection, process control, condition monitoring, fire prevention and monitoring, and continuous optical gas imaging.

Food production line quality control car windshield defrosting inspection
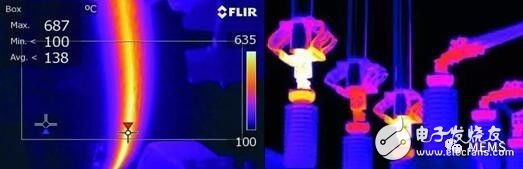
Thermal inspection of high-pressure equipment for positioning of pipes in automated welding machines

The hot spot on the ladle indicates that there may be a fault continuous monitoring warehouse

Detecting fire risk in the waste bin The transformer temperature is too high
The development potential of infrared thermal imaging cameras is huge, and the development of infrared thermal imaging in the golden development period has been promoted mainly by national defense applications. The latest products are mainly used in military products. The development of the decade has almost made this phenomenon a thing of the past. Today, thermal imaging is widely used in the large-scale development of markets such as fire protection, PVS, maritime, drones, robots, smart buildings, smart homes and smart stores, allowing infrared sensors. The application prospects in business are very optimistic. For example, FLIR, the leader in the thermal imaging market, has shipped 1 million Lepton movements in 2015 and has been integrated into more than 20 products (Lepton is a key infrared for FLIR). At the same time, FLIR has developed a smart strategy to introduce uncooled infrared imaging technology into a wide range of products for a variety of applications, enabling uncooled infrared imaging technology to be used more widely and to win a larger market. . As far as the domestic market is concerned, the infrared thermal imaging industry as a high-tech industry has broad prospects for development. According to incomplete statistics, the potential demand of China's infrared thermal imaging technology market can reach 50-60 billion yuan, and the current market situation is only in its infancy. By 2020, the infrared imaging market will grow by more than 20%. Domestic leading companies such as Gaode Infrared, Dali Technology, Hite Infrared, and Hikvision have also developed rapidly in the past decade, and new products and new applications have kept pace with the times. How does the thermal imaging camera work? Infrared thermography is a technique that converts an infrared image into a thermal radiation image, which reads temperature values ​​from an image and is a non-destructive testing technique. The Infrared Thermal Imager is a high-tech product that detects infrared radiation of a target object and converts the temperature distribution image of the target object into a video image through photoelectric conversion and electrical signal processing. How does the thermal imaging camera work? 1. The working range of the infrared thermal imager is in the natural world. As long as the temperature is higher than the absolute zero (-273 °C), the electromagnetic wave can be radiated. Infrared is the most widespread form of electromagnetic waves in nature. It is an energy that is invisible to the naked eye. Irregular movement of its own molecules and atoms produced by any object in a normal environment constantly radiates thermal infrared energy.
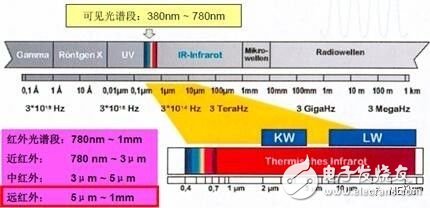
Infrared Thermal Imager Operating Spectroscopy Infrared is part of these electromagnetic waves. Together with visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, gamma rays and radio waves, it forms a complete continuous electromagnetic spectrum. As shown in the above figure, the wavelength range is from 0.78 μm to 1000 μm of electromagnetic radiation, which we call infrared radiation. Infrared radiation electromagnetic waves propagate in the air to be absorbed by the atmosphere, so that the energy of the radiation is attenuated. If the absorbed energy is too much, it cannot be observed by the thermal imager. The absorption of infrared rays, such as the atmosphere and smoke clouds, is also related to the wavelength of infrared radiation, and is transparent to infrared rays of 3 to 5 μm and 8 to 14 μm. Therefore, these two bands are called the "atmospheric window" of infrared rays. Using these two windows, the thermal imaging camera can be observed in a normal environment without the occurrence of infrared radiation attenuation. 2, the principle of thermal imaging Generally speaking, infrared thermal imaging is to change the invisible infrared radiation into a visible thermal image. The radiation abilities of different objects and even different parts of the same object and their reflection intensity to infrared rays are different. By using the difference between the radiation of the object and the background environment and the difference in the radiation of each part of the scene itself, the thermal image can show the undulations of various parts of the scene, so that the characteristics of the scene can be displayed. The thermal image is actually an image of the target surface temperature distribution. 3. The composition of the infrared camera The basic working principle of the infrared camera is: infrared rays are transmitted through the special optical lens and absorbed by the infrared detector. The detector converts the infrared signals of different strength into electrical signals, and then passes through Magnification and video processing to form a hot image for human eye to display on the screen. The camera consists of two basic parts: an optical system and a detector.
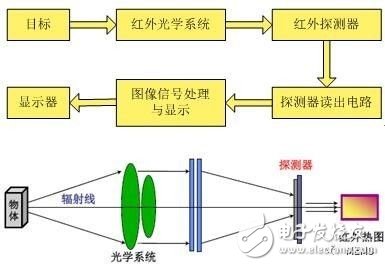
The working principle of the infrared camera is very sensitive and can detect the temperature difference less than 0.1 °C. For example, the FLIR thermal imaging camera can detect temperature changes as small as 0.02 ° C. With advanced detection technology and advanced mathematical algorithms, it can accurately measure the temperature of objects from -40 ° C to +2000 ° C. 4. Classification of infrared camera * According to the working temperature, it can be divided into a cooling type/uncooling type cooling type thermal imager. The detector is integrated with a low temperature refrigerator. This device can lower the temperature of the detector. In order to make the signal of thermal noise lower than the imaging signal, the imaging quality is better. For uncooled thermal imagers, the detectors do not require cryogenic refrigeration. The detectors used are usually based on microbolometers, mainly consisting of polysilicon and vanadium oxide detectors.

Cooling type thermal imager (left) and uncooled thermal imager (right) imaging effect * According to the function, it can be divided into temperature measuring type / non-temperature measuring type temperature measuring type infrared thermal imager, which can be directly read from the thermal image The temperature value at any point on the surface of the object, this system can be used as a non-destructive testing instrument, but the effective distance is relatively short. Non-temperature-measuring thermal imaging cameras can only observe the difference in thermal radiation on the surface of the object. This system can be used as an observation tool with a long effective distance.

Thermal image with temperature information Thermal image without temperature information The heart of the infrared camera - infrared detector infrared detector can be divided into: infrared photon detector and infrared heat detector.
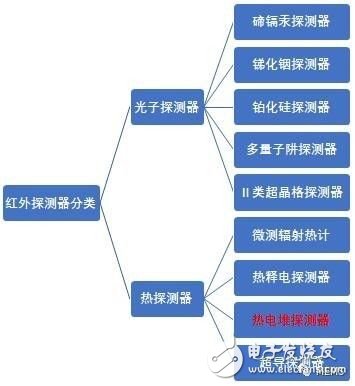
Specific classification of infrared detectors 1. Photon detector: The basic working principle is that when the detector absorbs photons of target or background radiation, the electrons in the outermost layer of the detector material transition to form free electrons in the crystal, resulting in photoconductivity or photovoltaic effect. The strength of the photoconductivity and photovoltaic effects depends on the radiation intensity of the radiation source and the sensitivity of the detector. The temperature of the photon detector remains substantially constant throughout the probing operation. 2. Heat detector: mainly by absorbing the energy of infrared radiation, causing the temperature of the detector to change, causing the change of the resistivity or the polarity of the detector. The change of the resistivity or the polarity of the heat detector also depends on the radiation source. Radiation intensity and detector sensitivity. 3, two types of infrared detector comparison: due to the different working mechanisms of the two, these two types of detectors show different infrared response characteristics: photon detector has the best response wavelength (peak wavelength), black body response rate and peak The difference in response rates varies greatly with the detector response band; the response rate of the heat detector is almost flat with wavelength. Therefore, there is almost no difference between the black body response and the peak response of the heat detector. On the other hand, the heat detector can have higher sensitivity than the photodetector as the detector operates at a higher temperature. Therefore, it is widely used in applications where the operating temperature is close to room temperature and is called an "uncooled" detector.

Infrared detectors operating at room temperature are examples of low-temperature operation of mercury cadmium telluride semiconductors 4. Infrared thermopile detectors Although infrared pyroelectric detectors have lower response sensitivity and longer thermal response time than other infrared detectors, in terms of device performance No competitive advantage. However, the thermopile detector fabrication is easy to be compatible with the integrated circuit process, the signal post-processing circuit is relatively simple, has the potential of low cost, and has certain application in the field of community security, safety monitoring, and automobile assisted driving with low infrared imaging image quality requirements. prospect. Therefore, the following specifically introduces you to the infrared thermopile detector. The infrared thermopile detector is a type of infrared heat detector. The thermopile is composed of a plurality of thermocouples connected in series, and has a larger output thermoelectric potential than the thermocouple. Earlier infrared thermopile detectors were obtained by depositing thermocouple materials onto plastic or ceramic substrates using mask vacuum coating, but the size of the device is large and difficult to mass produce. With the rapid development of microelectronics technology, the concept of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) was proposed, and micromachined infrared thermopile detectors were developed. The working principle of the infrared thermopile is the Seebeck Effect: if two different materials or materials have the same work function A and B with different work functions, they are connected at the hot junction, and there is a temperature difference dT between the hot junction and the cold junction. Then, an open circuit potential dV is generated between the two cold junctions. In order to improve the performance of the detector, the ideal thermocouple material should be characterized by low thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity and high Seebeck coefficient, but in fact these factors also have an influence on each other, defined by a quality factor Z.
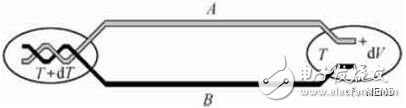
The Seebeck effect diagram (A and B in the figure constitute a pair of thermocouples) The application fields of infrared thermopile sensors are: health field (ear temperature gun, fore temperature gun, pressure sensor, baby incubator, etc.), industrial field (measurement) Temperature gun, copier, charging overheat protection, transformer box, etc.), security field (abnormal temperature screening, etc.), home appliance field (microwave oven, induction cooker, cooker, hair dryer, dryer, electric heater, etc.), lighting field (LED control Switch), automotive field (in-car air conditioning and exhaust, etc.).

glitter keychain,luminous keychains,glitter keychain molds,keychains bulk,keychain wholesale,shiny keychain
Shenzhen Konchang Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.konchang.com